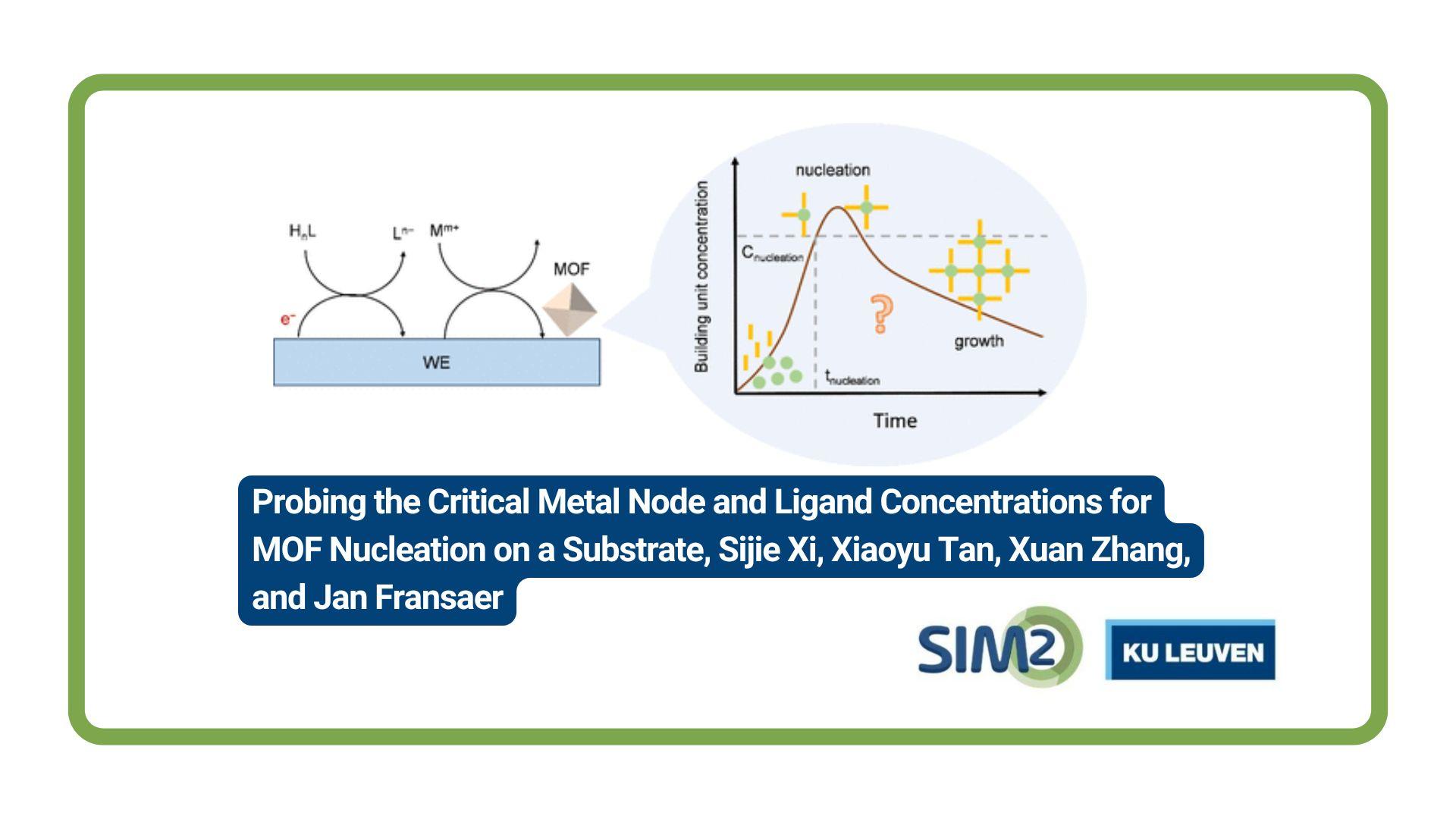
Sijie Xie and colleagues from the Department of Materials Engineering, KU Leuven, have published a new letter entitled Probing the Critical Metal Node and Ligand Concentrations for MOF Nucleation on a Substrate. The letter is published in the March 2025 edition of ACS Materials Letters.
Determining the critical concentrations of metal nodes and ligands required for metal–organic framework (MOF) nucleation on a substrate remains a fundamental challenge. Here we propose an electrochemical method to address this issue by integrating in situ surface mass change analysis with in situ surface pH measurement during a cathodic deposition process. Taking UTSA-280 ([Ca(C4O4)]n) as an example, the critical metal ion (c(Ca2+)) and deprotonated ligand (c(C4O42–)) concentrations for UTSA-280 nucleation on a gold substrate are determined. It is found that the values of c(Ca2+) × c(C4O42–) in different electrolytes with varied bulk Ca2+ concentrations are similar, which can be seen as an analogue of the solubility product of UTSA-280 considering its chemical formula. Also, a simple yet previously overlooked strategy to shorten the incubation time for MOF nucleation in cathodic deposition is proposed and verified. The presented method can be applied to other MOFs.
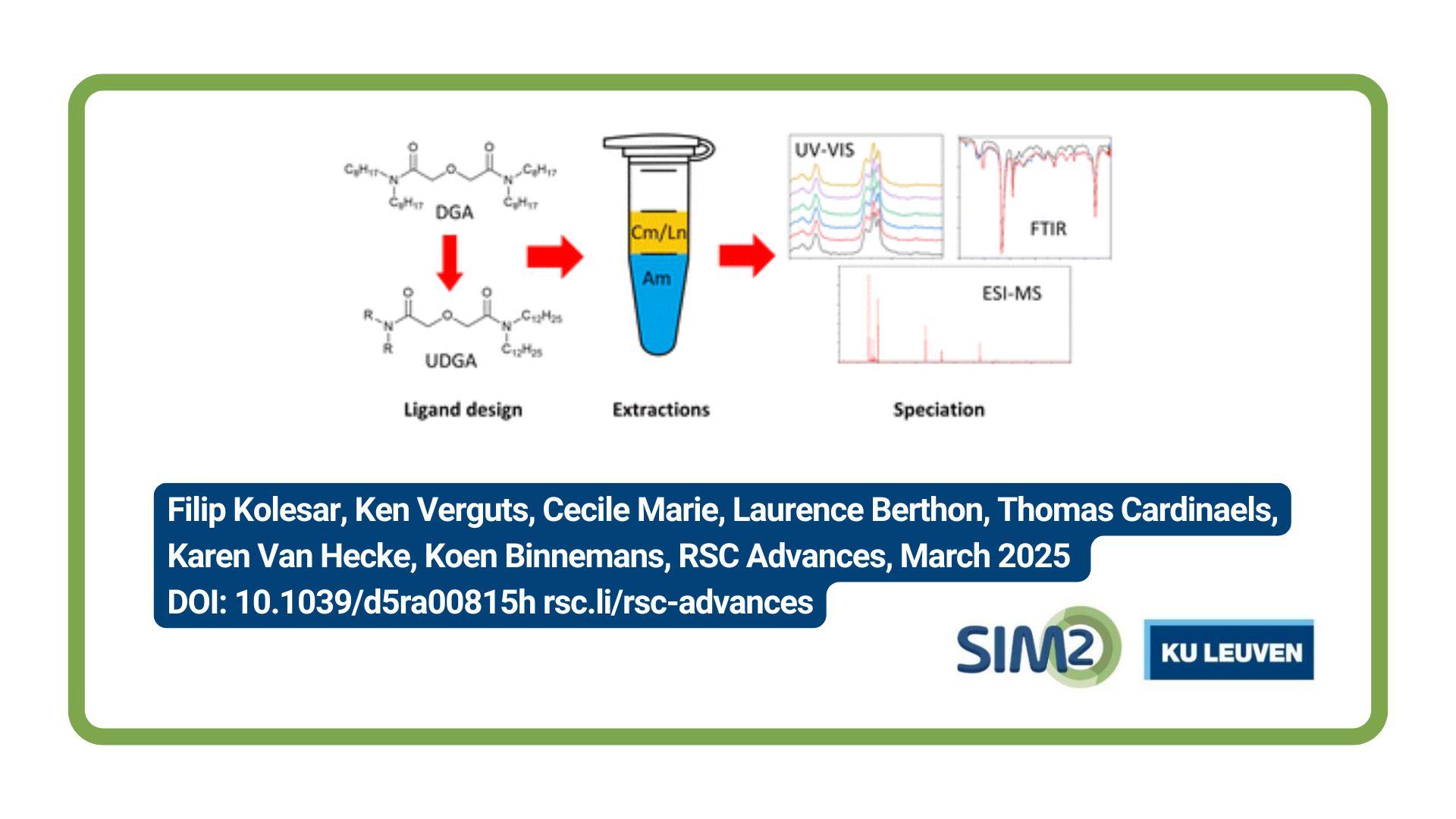
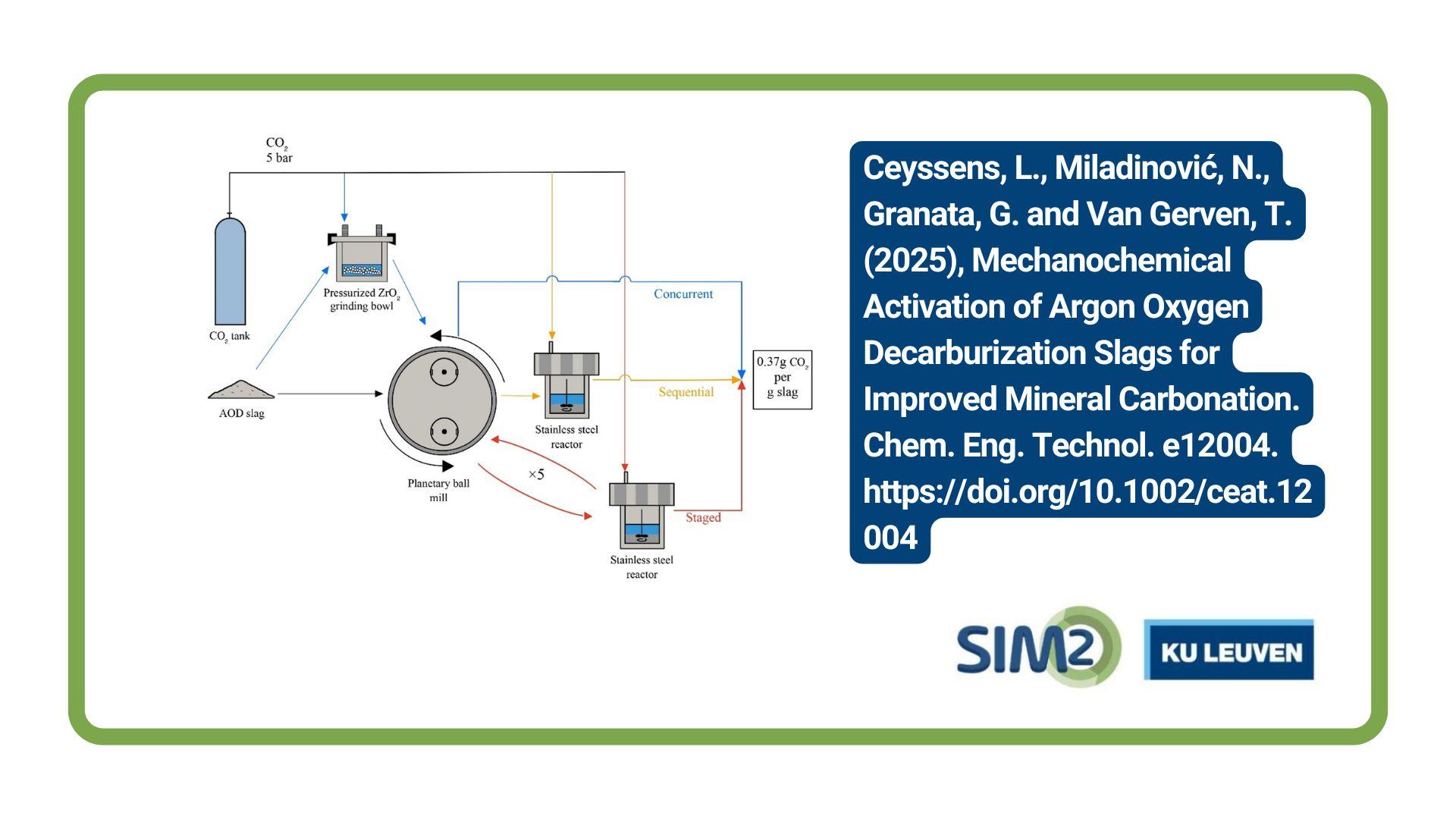
Reference