Simon Bellens and colleagues from KU Leuven have published a new review of machine learning in industrial X-ray computed tomography. The articl is published in the July issue of the CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology.
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) has been shown to be a reliable tool for quality inspection, material evaluation, and dimensional measurement tasks across diverse academic and industrial applications. In recent years, the integration of machine learning and deep learning techniques have ushered new advances in the industrial computed tomography domain spanning multiple facets, including image reconstruction, segmentation, and feature characterization. This review paper comprehensively surveys the current state-of-the-art machine learning and deep learning applications throughout the entire XCT workflow. Additionally, we explore relevant developments in the medical imaging domain, evaluating their implications for industrial computed tomography. In conclusion, we identify potential future research, drawing insights from existing research gaps in the domain and recent advancements in artificial intelligence. Notably, we underscore the importance of uncertainty quantification and model explainability for further acceptance of artificial intelligence techniques in the domain.
Reference
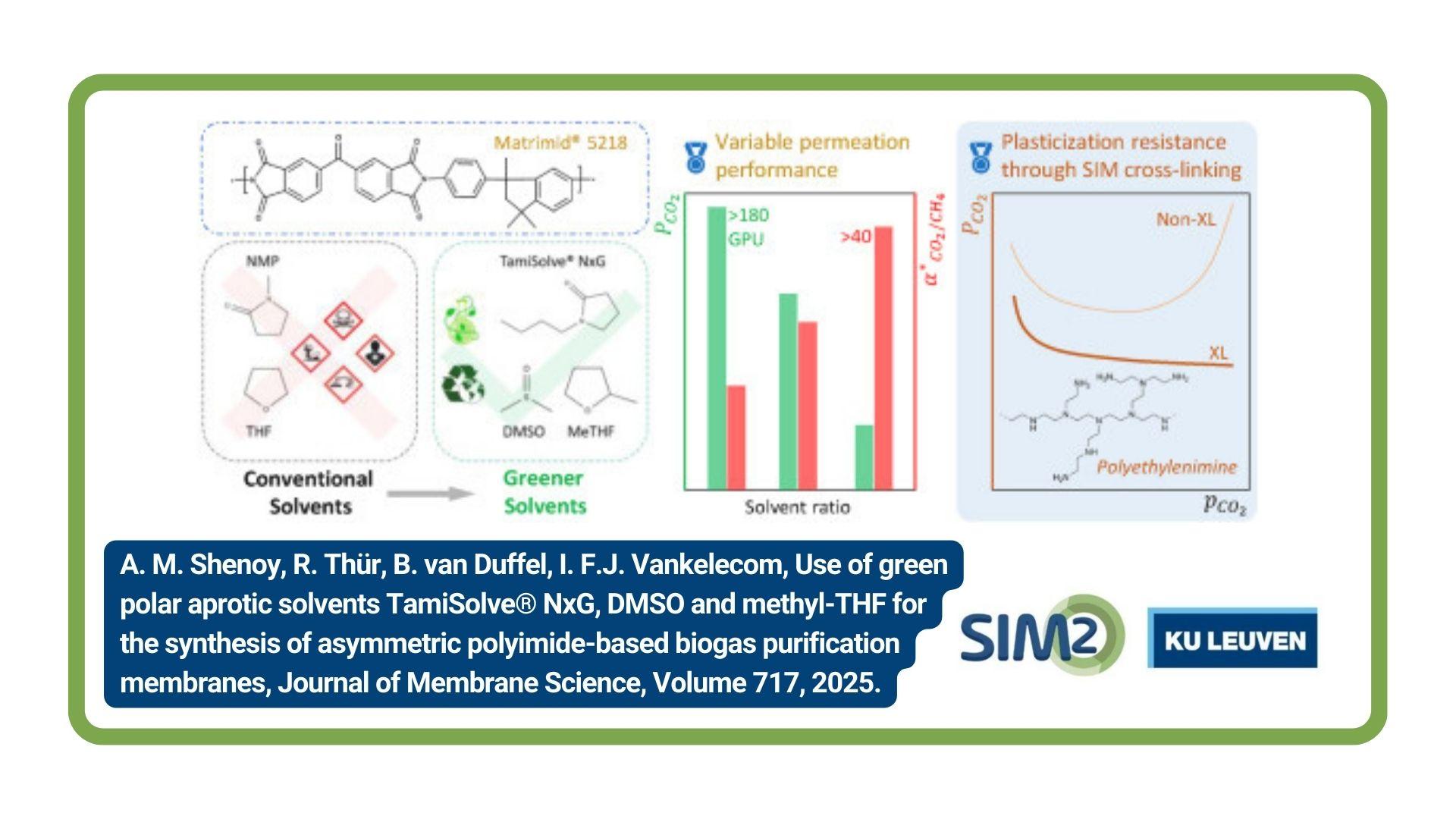
Simon Bellens, Patricio Guerrero, Patrick Vandewalle, Wim Dewulf,Machine learning in industrial X-ray computed t omography – a review, CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, Volume 51, 2024, Pages 324-341, ISSN 1755-5817, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2024.05.004.