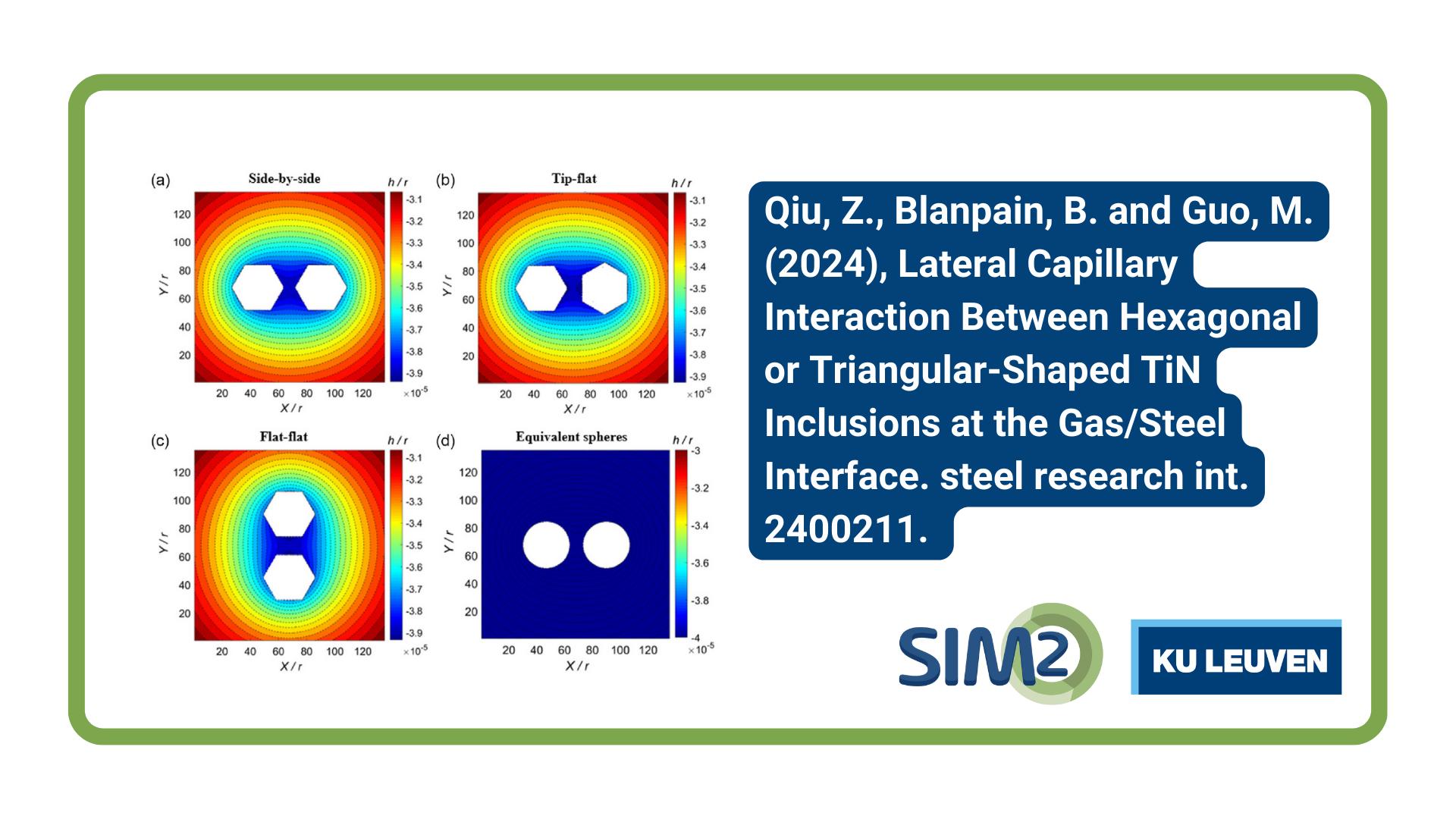
Zilong Qiu, Bart Blanpain and Muxing Guo, members of KU Leuven’s Department of Materials Engineering, have published a new Research Article in Steel Research International. They report on their latest research into the capillary interactions between triangular and hexagonal TiN inclusions at the gas/steel interface using analytical and numerical capillary models.
Understanding the behaviour of non-metallic inclusions at the gas/steel interface is essential for the removal of inclusions from molten steel. The capillary interaction between triangular and hexagonal TiN inclusions at the gas/steel interface has been quantitatively evaluated using the analytical solution and the newly developed sub-particle model. The analytical solution, which simplifies inclusions into spheres, overestimates the capillary force by 3 and 10 times for triangular and hexagonal inclusions. The meniscus shapes around the particles and the long-range capillary forces are dependent on the separation distance and their mutual orientation. At a constant centre-to-centre distance, the tip–flat and the side-by-side configurations give the strongest capillary interaction for triangular and hexagonal inclusions, respectively. In contrast, the flat–flat configuration is the preferred agglomeration pattern if the surface-to-surface distance is constant. The discrepancy might come from the more complex meniscus shapes around the real particles.
Reference
Qiu, Z., Blanpain, B. and Guo, M. (2024), Lateral Capillary Interaction Between Hexagonal or Triangular-Shaped TiN Inclusions at the Gas/Steel Interface. steel research int. 2400211. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.202400211
Acknowledgement
Z.Q. gratefully acknowledges the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for financial support (File No. 201706080018).